Web the term open reading frame (orf) is of central importance to gene finding. These introns are then removed to make a functioning messenger rna (mrna) that can be translated into a protein. An open reading frame, as related to genomics, is a portion of a dna sequence that does not include a stop codon (which functions as a stop signal). Web not all augs are actually used as the first codon in translation, in fact, most are either internal to a translated protein or not translated at all. In genes that lack introns (e.g.
The coding sequence (cds) is the actual region of dna that is translated to form proteins. As the genetic code is read in nonoverlapping triplets ( codon s) there are three possible ways of trans lating a sequence of nucleotides into a protein , each with a different starting point. Web not all augs are actually used as the first codon in translation, in fact, most are either internal to a translated protein or not translated at all. That's a pretty abstract concept, so let's look at an example to understand it better. Web small peptides of 100 amino acids or fewer are encoded by small open reading frames (smorfs) and mediate key physiological functions in animals and humans.
That's a pretty abstract concept, so let's look at an example to understand it better. Since each coding unit ( codon ) of the genetic code consists of three consecutive bases, the reading frame is established according to precisely where translation starts. An open reading frame can be within another open reading frame. Web a reading frame is a sequence of nucleotide triplets that are read as codons specifying amino acids; An exon is a coding region of a gene that contains the information required to encode a protein.
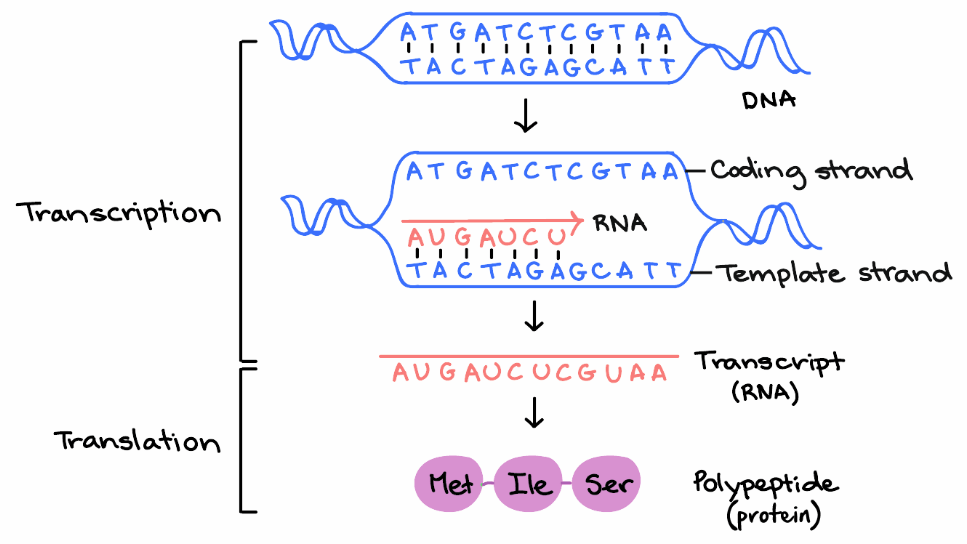
While the orf may contain introns as well, the cds refers to those nucleotides (concatenated exons) that can be divided into codons which are actually translated into amino acids by the ribosomal translation machinery. Web reading frame determines how the mrna sequence is divided up into codons during translation. Web every region of dna has six possible reading frames, three in each direction. The mrna below can encode three totally different proteins, depending on the frame in which it's read: Orfs occur randomly and abundantly across the whole genome. Where these triplets equate to amino acids or stop signals during translation, they are called codons. That's a pretty abstract concept, so let's look at an example to understand it better. Of these, only a fraction make their way into transcripts and only some of these end up being translated. Most prokaryotic genes), an orf in the dna sequence will define the entire translated region. Surprisingly, at least three definitions are in use. An open reading frame can be within another open reading frame. These introns are then removed to make a functioning messenger rna (mrna) that can be translated into a protein. The reading frame that is used determines which amino acids will be encoded by a gene. Web reading frame a sequence of bases in messenger rna (or deduced from dna) that encodes for a polypeptide. In analysis of a dna sequence, an orf is characterized by the sequence of nucleotides that when transcribed into mrna results in a series of triplet codon s that is not interrupted by a translation termination codon.
These Introns Are Then Removed To Make A Functioning Messenger Rna (Mrna) That Can Be Translated Into A Protein.
In molecular biology, open reading frames ( orfs) are defined as spans of dna sequence between the start and stop codons. There are 3 possible reading frames in a mrna strand and six in a double stranded dna molecule due to the two strands from which transcription is possible. A single strand of dna sequence has three possible reading frames. Web the meaning of reading frame is a sequence of nucleotide triplets that is potentially translatable into a polypeptide and that is determined by the placement of a codon that initiates translation.
Web Overview Reading Frame Quick Reference A Sequence Of Bases In Messenger Rna (Or Deduced From Dna) That Encodes For A Polypeptide.
Orfs occur randomly and abundantly across the whole genome. Web not all augs are actually used as the first codon in translation, in fact, most are either internal to a translated protein or not translated at all. Web small peptides of 100 amino acids or fewer are encoded by small open reading frames (smorfs) and mediate key physiological functions in animals and humans. Web reading frame one of the three possible ways of reading a nucleotide sequence.
Since Each Coding Unit (Codon) Of The Genetic Code Consists Of Three Consecutive Bases, The Reading Frame Is Established According To Precisely Where Translation Starts.
Web open reading frames (orfs) are defined as spans of dna sequence between start and stop codons. Start codons are highlighted in purple, and stop codons are highlighted in red. There can be no additional stop codons within that sequence. Web open reading frame (orf) one of three possible reading frames in which an mrna is potentially translated into protein.
An Open Reading Frame Is Any Sequence Starting From An Aug To A Stop Codon.
Web open reading frames are part of reading frames that does not contain stop codons in other words open reading frame is the region of the nucleotide sequence from the start codon to stop codon. Web these are called reading frames. In analysis of a dna sequence, an orf is characterized by the sequence of nucleotides that when transcribed into mrna results in a series of triplet codon s that is not interrupted by a translation termination codon. An open reading frame can be within another open reading frame.








![Open Reading Frame [ORF] Definition, Role in Protein Synthesis and](https://i.pinimg.com/originals/fd/b2/a0/fdb2a07b74b89eb88e7de6e8ccc793fb.jpg)